 | 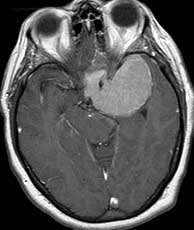 | 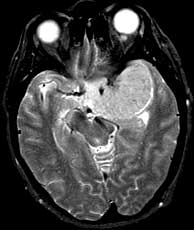 |
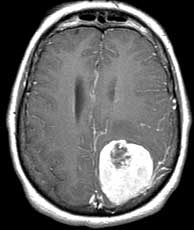
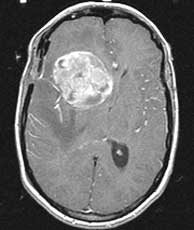
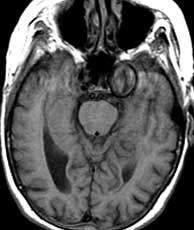
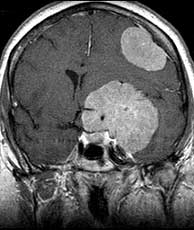
| T1 post-gad | T1 post-gad | T2 |
Diagnosis: Meningiomas
Meningiomas are usually dural based, intensely enhancing extraaxial masses presenting in woman between the ages of 40 and 60 containing progesterone and estrogen receptors. They are the most common primary CNS tumor of non-glial origin. Typical locations are parasagittal, over the convexities and the sphenoid ridge. They may be seen in association with neurofibromatosis type II and are multiple in up to 9% of patients, many of whom have NF II. Meningiomas are intraventricular in 2% of cases. They are hyperdense on CT and 1/4 may have some calcification. Hemorrhage is unusual but cystic change may be seen. Meningiomas are typically isointense to gray matter on T1 while T2 signal is more variable. A dural tail may be present due to their extraaxial location as well as hyperostosis of the overlying calvarium. A metastasis may rarely be dural based and simulate a meningioma. However, in this case, dural based metastases of this size without invasion or necrosis would be very unusual. Related Cases