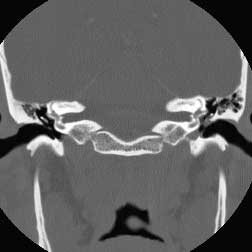
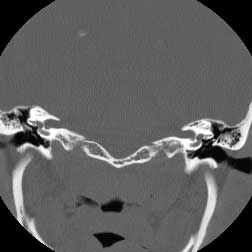
 | 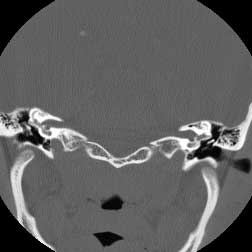 |
| Coronal CT BW post | Coronal CT BW ant |
Diagnosis: Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatomas may be either cogenital or acquired (98%) as a complication of chronic otitis. They arise from either the pars flaccida or tensa of the tympanic membrane. Pars flaccida cholesteatomas occupy Prussak's space and are also known as attic cholesteatomas. Pars tensa cholesteatomas are usually located more posteroinferiorly. This case has the classic appearance of an acquired attic cholesteatoma; soft tissue in Prussak's space, medial displacement of the ossicles and erosion of the scutum. Chronic otitis media may be differentiated from cholesteatoma due to its lack of associated bony erosion althought it may often co-exist with cholesteatoma. Glomus tympanicum is in the general differential of middle ear masses, but is not included here since it is found on the cochlear promontory or in the hypotympanum not in Prussaks space Related Cases